Naukowcy znaleźli odpowiedź na pytanie zadane w tytule. Najzimniejszym miejscem na świecie okazuje się być mgławica w kosmosie albo jedno z laboratoriów MIT.
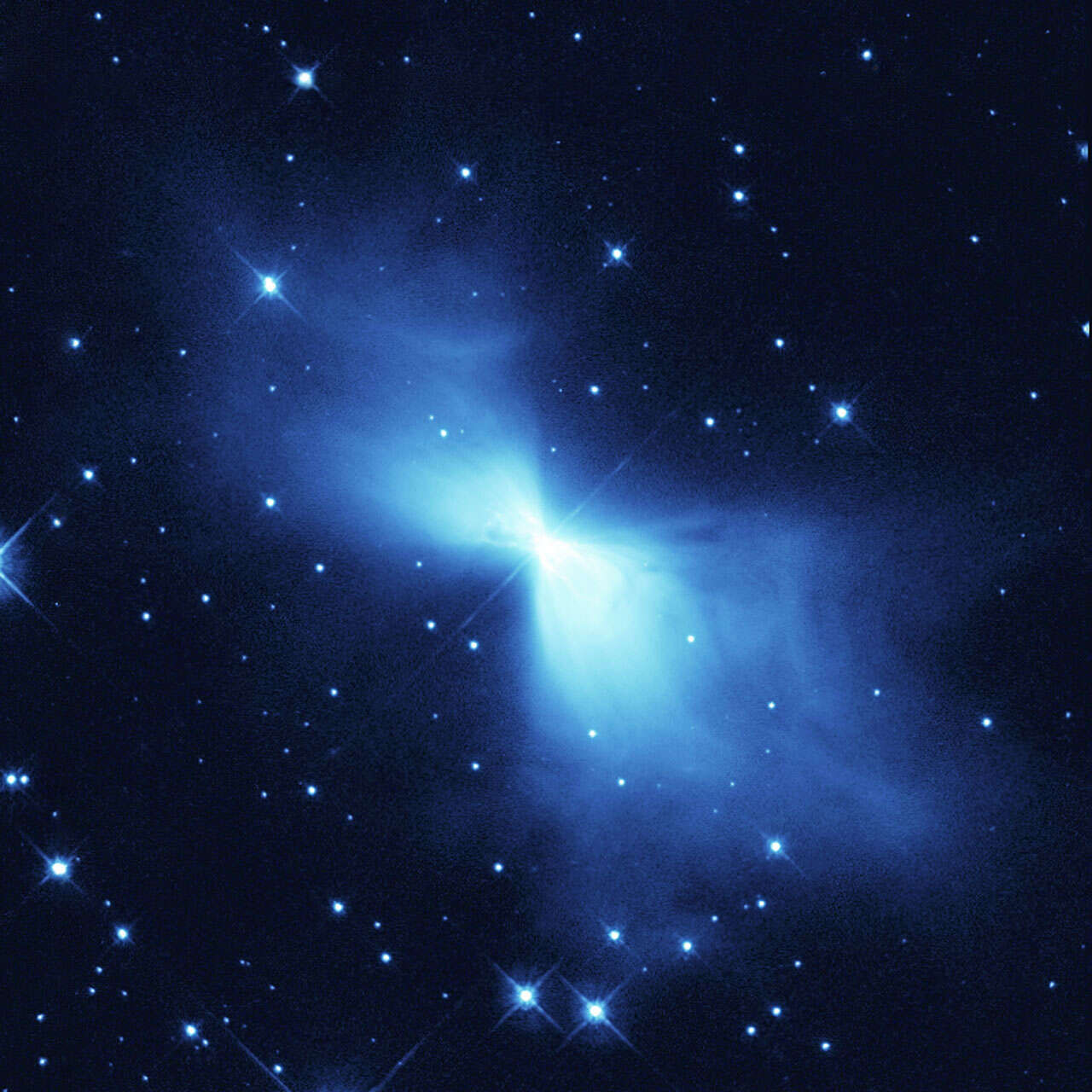
Mgławica Boomerang, która jest pomieszaniem pyłów i zjonizowanych gazów, ma średnią temperaturę równą -272°C, czyli zaledwie 1°C powyżej zera bezwzględnego. Mgławica znajduje się 5 tysięcy lat świetnych od Ziemi i posiada umierającą gwiazdę w środku. Jak to możliwe, że gwiazda nagle staje się tak zimna? Otóż, kiedy ona spala wodór ze swojego jądra, jej jasność wzrasta. Dzieje się tak bowiem gwiazda nie jest w stanie wytworzyć na tyle ciepła, aby utrzymać swój ciężar. Pozostały wodór zaczyna ulegać ściśnięciu. Taka kompresja generuje więcej energii, ale gwiazda staje się jednocześnie bardziej „opuchnięta”. Tak więc mimo, że gwiazda jest jaśniejsza to jej gazy są chłodniejsze oraz wygląda ona na bardziej czerwoną. W końcu spala ona całkowicie swój wodór i w tym momencie zamienia się ona w białego karła. Rezultatem tego jest powstanie świetnie wyglądających mgławic. Gaz z nich porusza się bardzo szybko, dlatego też możliwe jest uzyskanie tak niskich temperatur.
Jeszcze zimniejsze jest jedno z laboratoriów w MIT, gdzie naukowcy w 2015 roku uzyskali temperaturę równą -273,15°C. Wykorzystali oni lasery do chłodzenia atomów sodu i potasu i dzięki temu możliwe było uzyskanie tak niskiej wartości.
Źródło: https://www.livescience.com